‘Colonies problem’: Delegate’s mic cut after outcry during House speaker vote
Ukraine: How the war shifted in 2024
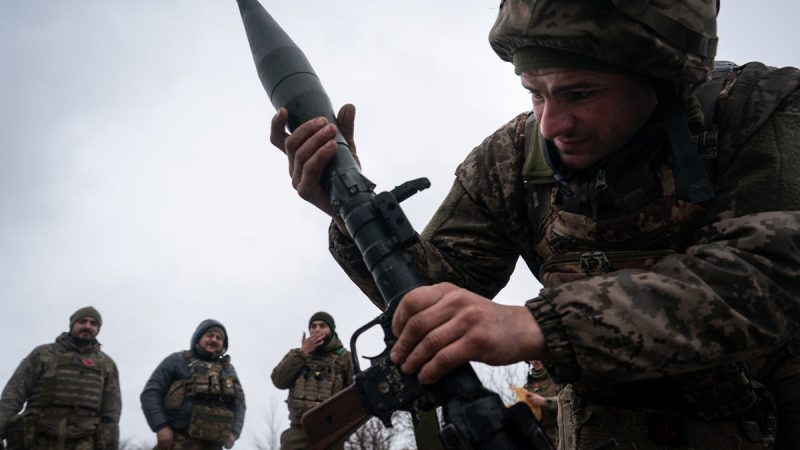

As the third year of war in Ukraine nears a close as the new year approaches and ahead of the Feb. 24, 2025, anniversary date, new battle lines have once again been established after Russia made advances in the east and Kyiv opened a new battlefront, this time in Russia.
The war that had already plagued Europe, the U.S. and, to an extent, the Middle East, costing a whopping $278 billion in aid for Ukraine, including nearly $87 billion from Washington, expanded to Asia in 2024 as geopolitical rivalries in the Indo-Pacific began playing out through proxy in Ukraine.
SETTING THE TONE
2024 began with a heated fight in Congress over whether the U.S. should supply more military aid to Ukraine, a fight that highlighted major divisions in the Republican Party and Kyiv’s deep reliance on Washington’s military support.
The monthslong debate, which finally ended in April, had major implications for Ukraine when it came to its ability to defend against Moscow’s missiles and its ability to counter Russian offenses. In 2023, Russia was unable to make any major advances despite the sheer number of men the Kremlin has long been able to throw into its war machine.
But 2024 politics in the U.S. changed the reality of war for Ukraine.
The stalled supplies not only significantly increased Ukraine’s vulnerabilities in the east, particularly in Donetsk, it enhanced frustration from Kyiv, NATO allies and those who argued that defending Ukraine is in the U.S.’s security interest. It escalated attention around the Biden administration’s strike bans on U.S.-supplied long-range missiles, which the president eventually lifted in November.
As U.S. politics at home grew increasingly volatile ahead of the presidential election, uncertainty mounted over what another Trump White House could mean for Kyiv; a question that has already had other geopolitical consequences.
COST OF WAR
In late April, the House passed a $61 billion military aid package for Ukraine that pushed U.S. financial commitments to $183 billion since Russia first launched its invasion in 2022. The package was meant to prompt an immediate surge in the delivery of military equipment and supplies, which, according to the Center for Strategic and International Studies, had fallen to 10% of what it had been the year before.
The European Union in June officially began membership talks with Ukraine after determining Kyiv had met the necessary requirements to join an economic and political partnership by countering corruption, reining in political lobbying, increasing transparency around officials’ wealth and bolstering the rights of national minorities.
By the July NATO Summit in Washington, D.C., some members began ramping up pressure on the Biden administration, along with other allies like the U.K. and Germany, to lift any and all strike restrictions enforced on Ukraine, which prevented Kyiv from hitting military targets and weapons depots deep inside Russia, a move Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy repeatedly said was needed to better stop Russia’s missile and drone attacks.
Moscow in September looked to secure its defense budget for 2025, and the federal government submitted a plan to its State Duma that called for $183 billion to be allocated for national security and defense next year, which amounted to some 41% of its annual expenditures, according to the Institute for the Study of War.
That figure appeared to have been whittled down by the time it reached Russian President Vladimir Putin’s desk in early December as he signed off on a 13.5 trillion ruble plan ($124 million), and it accounts for 32.5% of Russia’s 2025 budget, according to the Associated Press.
In October, the G-7 finalized a $50 billion loan to Ukraine that would be paid using frozen Russian assets, and on Christmas Eve, Ukrainian Prime Minister Denys Shmyhal said Kyiv had received its first $1 billion from the U.S.
The U.S. has agreed to send Kyiv $20 billion in frozen asset profits to be used for Ukraine’s military and reconstruction assistance through 2025.
President Biden has vowed to fast-track as much military assistance to Ukraine as he can during the final days in office.
ESCALATION
Throughout the war, Russia has relied on a heavy missile and drone campaign to brutalize the entirety of Ukraine. But in 2024, Moscow escalated its aerial attacks targeting towns and cities, particularly in eastern Ukraine, ahead of its infantry advances, even if it meant the complete decimation of urban areas.
2024 saw more battlefield movement than 2023, though according to data provided by the Institute for the Study of War, this was largely seen in the second half of the year, a price for which Russian paid heavily.
November proved to be a particularly brutal month, with Russia seeing its highest battlefield losses ever with 45,720 casualties reported in November, which was up from nearly 42,000 in October, along with an estimated $3 billion worth of military equipment, according to the Ukrainian Ministry of Defense.
Moscow also twice set the record for the greatest number of drone strikes it levied against Ukraine in a single campaign since the war began, first with 145 drones fired overnight on Nov. 9, followed by 188 strikes beginning the night of Nov. 25.
After more than a year of a relatively stagnant front line, Russia in May launched a new front in Kharkiv, which Ukraine had liberated in 2022, though the Kremlin’s renewed offensive largely failed.
By early August, Ukraine made international headlines when it launched a surprise ground incursion into Russia’s Kursk region. It was an apparent attempt to divert forces from eastern Ukraine to the Kremlin’s home turf and give it a bargaining chip when the time comes for peace negotiations.
The campaign was the largest attack on Russia since World War II, and by mid-October the Pentagon had confirmed that North Korea had deployed troops to Russia, with some 11,000 North Korean soldiers believed to be fighting Ukraine in Kursk, the first foreign nation to send in troops since the war began.
Though North Korea is not the only nation to aid Russia in its invasion, Iran has for years been sending Shahed drones. In September, the U.S. accused Iran of supplying Russia with short-range ballistic missiles.
Ukraine is estimated to have lost 40% of the land it initially seized in Russia, according to reports last month. But North Korea is also reported to have endured heavy losses, with Zelenskyy claiming this week that 3,000 North Korean troops had been killed in the fighting while others face extreme logistical shortages, including access to clean water, the Associated Press reported.
China has also been accused of aiding Russia by covertly sending it military support in the form of microelectronics and semiconductors, among other items.
YEAR END
North Korea’s direct involvement in Russia’s war has further highlighted the divisions in the Indo-Pacific that have arisen in recent years, not only in the face of Chinese aggression, but Pyongyang’s, which is a dynamic that has become caught up in the largest war Europe has seen since World War II as Japan and South Korea increasingly back Western allies and view the Russia-North Korea alliance as a threat.
North Korea’s deployment of troops to Russia reportedly prompted South Korea to consider escalating its non-lethal aid by mulling over a supply of missiles. Japan on Christmas Day sent Ukraine $3 billion in frozen Russian assets, adding to the $12 billion Tokyo has provided to Kyiv. In addition, Japan also pledged to support Ukraine’s energy sector, which Russia routinely targets.
Russia once again solidified its primary winter strategy by attacking Ukraine’s energy infrastructure on Christmas Day by firing 184 drones and missiles across the country, according to Ukraine’s air force. The attacks sparked mass blackouts amid freezing temperatures in multiple regions, including Kharkiv in the north, the central Dnipropetrovsk and Poltava areas, as well as Ivano-Frankivsk in western Ukraine.
Zelenskyy condemned the attacks as ‘inhumane.’
Former President Trump said on the campaign trail that he would end the war before even entering office. Since winning the election, the president-elect’s confidence in his ability to do that appears to have shifted.
Speaking at his first press conference this month since securing a second term, he said, ‘We’re trying to get the war stopped, that horrible, horrible war that is going on in Ukraine with Russia. We’ve got a little progress. It is a tough one, it is a nasty one.’
Trump has said he will work to secure a peace deal between Putin and Zelenskyy, which the Ukrainian president this month suggested he would be open to, though there are major stipulations on which Putin is unlikely to agree, such as a future for Kyiv in the NATO alliance.
Additionally, Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov dismissed Trump’s calls for a ceasefire and said a ‘ceasefire is a road to nowhere,’ suggesting Trump could face a tough diplomatic future.